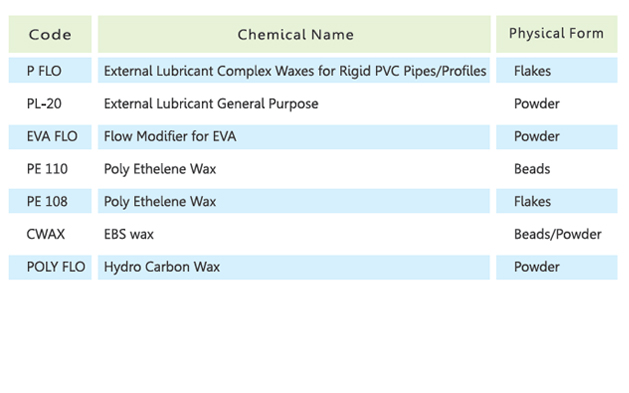

Lubricants are divided into two areas, internal and external lubricants. However, the transition between the effect of external and internal lubrication is fluid: internal lubricants often also have some effect of external lubrication and vice versa. Lubricants that have both effects are called "combined lubricants".
Internal lubricants reduce the frictional forces that occur between chains of PVC molecules, which reduces the viscosity of the melt. They are polar and therefore very compatible with PVC. They help achieve excellent transparency even at high doses and do not tend to ooze, which optimizes the welding, bonding and printing properties of the final product.
External lubricants reduce the adhesion between PVC and metal surfaces. They are mainly non-polar, like paraffin waxes and polyethylene. The effect of external lubrication is largely determined by the length of the hydrocarbon chain, its branching and its functional group. In large doses, they can cause clouding and exudation.